A new research has shown that climate change could lead to half a million more deaths from malaria in Africa over the next 25 years.
The study, which was published in Nature, finds that extreme weather, rising temperatures and shifting rainfall patterns could result in an additional 123m cases of malaria across Africa – even if current climate pledges are met.
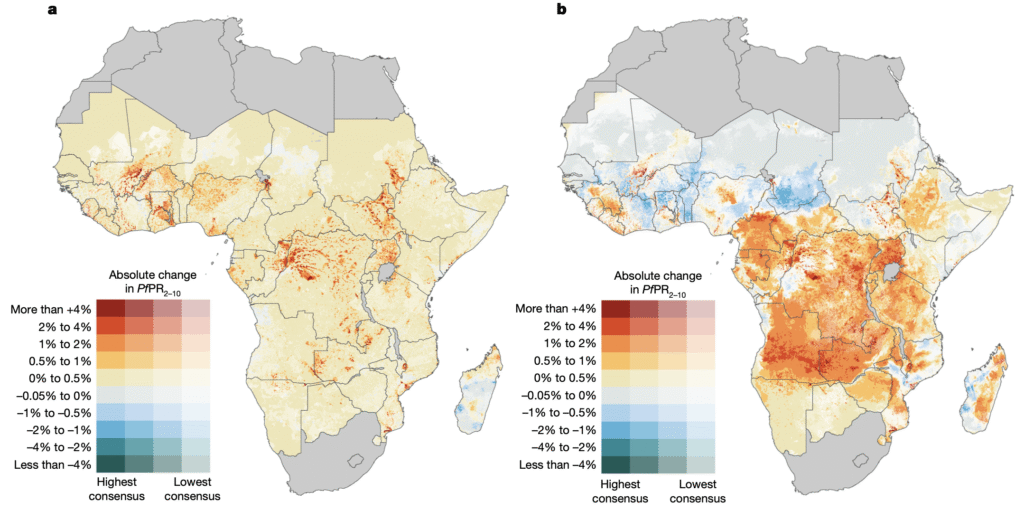
The authors explain that as the climate warms, “disruptive” weather extremes, such as flooding, will worsen across much of Africa, causing widespread interruptions to malaria treatment programmes and damage to housing. These disruptions will account for 79% of the increased malaria transmission risk and 93% of additional deaths from the disease, according to the study.
The rest of the rise in malaria cases over the next 25 years is due to rising temperatures and shifting rainfall patterns, which will change the habitable range for the mosquitoes that carry the disease, the paper says. The majority of new cases will occur in areas already suitable for malaria, rather than in new regions, according to the paper.
The study authors tell Carbon Brief that current literature on climate change and malaria “often overlooks how heavily malaria risk in Africa is today shaped by climate-fragile prevention and treatment systems”.
The research shows the importance of ensuring that malaria control and primary healthcare is “resilient” to the extreme weather, they say.
Read also: Floods kill more than 100 across southern Africa as rains intensify
Malaria kills hundreds of thousands of people every year. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 610,000 people died due to the disease in 2024. In 2024, Africa was home to 95% of malaria cases and deaths. Children under the age of five made up three-quarters of all African malaria deaths.
The disease is transmitted to humans by bites from mosquitoes infected with the malaria parasite. The insects thrive in high temperatures of around 29C and need stagnant or slow-moving water in which to lay their eggs. As such, the areas where malaria can be transmitted are heavily dependent on the climate.
There is a wide body of research exploring the links between climate change and malaria transmission. Studies routinely find that as temperatures rise and rainfall patterns shift, the area of suitable land for malaria transmission is expanding across much of the world.
Study authors Prof Peter Gething and Prof Tasmin Symons are researchers at the Curtin University’s school of population health and the Malaria Atlas Project from the The Kids Research Institute, Australia.
They tell Carbon Brief that this approach does not capture the full picture, arguing that current literature on climate change and malaria “often overlooks how heavily malaria risk in Africa is today shaped by climate-fragile prevention and treatment systems”.
The paper notes that extreme weather events are regularly linked to surges in malaria cases across Africa and Asia. This is, in-part, because storms, heavy rainfall and floods leave pools of standing water where mosquitoes can breed. For example, nearly 15,000 cases of malaria were reported in the aftermath of Cyclone Idai hitting Mozambique in 2019.
However, the study authors also note that weather extremes often cause widespread disruption, which can limit access to healthcare, damage housing or disrupt preventative measures such as mosquito nets. These factors can all increase vulnerability to malaria, driving the spread of the disease.
In their study, the authors assess both the “ecological” effects of climate change – the impacts of temperature and rainfall changes on mosquito populations – and the “disruptive” effects of extreme weather.
Story was adapted from Carbon Brief.