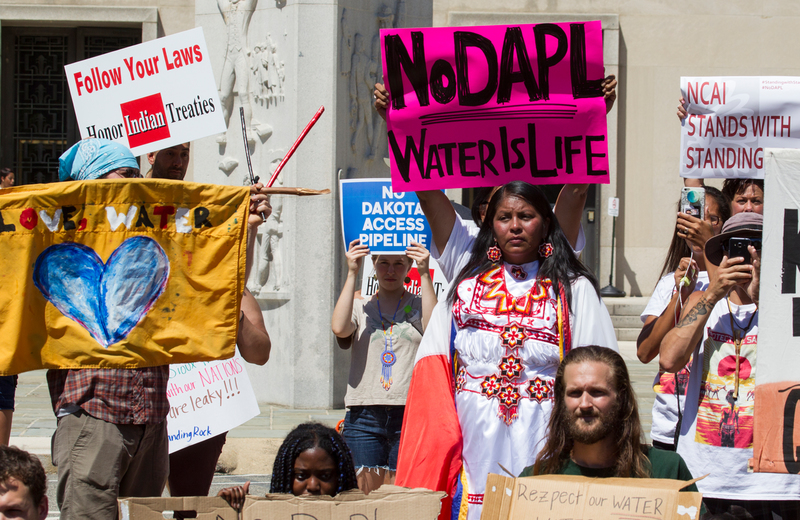Latest reports have shown that organisations and campaigners across the climate justice movement are joining forces to counter the wider chilling effect of a major legal blow that could bankrupt one of its largest players.
It will be recalled that earlier this week, a jury in the US state of North Dakota found Greenpeace International and its US bodies guilty of a mix of defamation, trespass, nuisance and conspiracy – and ordered them to pay more than US$660 million in damages to oil pipeline company Energy Transfer.
The lawsuit related to protests against the Dakota Access pipeline in 2016 and 2017. These actions, centered around the Standing Rock Sioux Reservation, brought Indigenous activists fighting for water rights together with climate campaigners challenging the company’s planned transmission of oil from North Dakota to Illinois. They did not stop the pipeline from being completed, but caused major disruption.
According to reports, Energy Transfer had previously sought damages against Greenpeace and others in a federal lawsuit that was dismissed in 2019.
Read also: Experts seeks adaptation of strategies to protect women against climate change impacts
But this time the claim was successful. Energy Transfer’s legal team successfully argued during the court proceedings that Greenpeace had “incited” the disruption. Greenpeace contended that its US bodies only played a small role, and the international group itself merely signed a letter opposing the project.
Energy Transfer called it “a resounding verdict”, declaring Greenpeace’s actions “wrong, unlawful, and unacceptable by societal standards”, adding that it “is a day of reckoning and accountability for Greenpeace”. But Greenpeace US bodies have said they will appeal and Greenpeace International is “weighing all legal options”.
Greenpeace, which has campaigned on a wide range of environmental matters since the 1970s, acknowledges there is a risk of bankruptcy due to the damages awarded against it. However, it maintains this is “very remote” for its international arm whose assets are located in the Netherlands, where the verdict is “very unlikely to be recognised by Dutch courts”. Greenpeace’s 25 other branches around the world are expected to keep functioning as normal.
The case has been classified as a strategic lawsuit against public participation (SLAPP). These cases, which arose in the United States in the 1970s and ’80s, can take various forms across different jurisdictions. But legal experts say they are an increasingly popular “lawfare” tactic used by powerful companies and individuals around the world – and many cases relate to the environment.
Story was adapted from Climate Home News.