A group of researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has proposed that the worst impact of climate change can be mitigated with space bubbles.
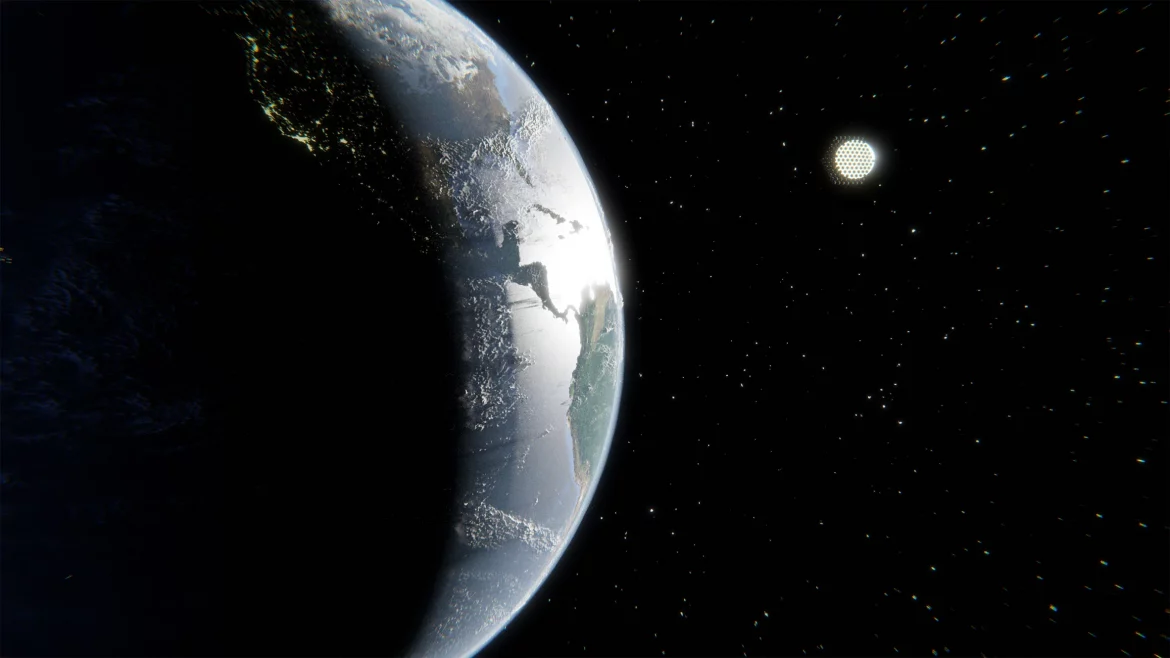
The scientists have already outlined what they refer to as a strategy in which a huge raft of bubbles, carefully positioned between Earth and the Sun, would deflect sunlight (and thus heat) to stop further global warming.
According to a web page dedicated to the solution, “Geoengineering might be the final and only option,”. “Yet, most geoengineering proposals are earth-bound, which poses tremendous risks to our living ecosystem,”.
The scientists said that “If we deflect 1.8% of incident solar radiation before it hits our planet, we could fully reverse today’s global warming. They add that the bubble array would be made of inflatable shields of thin silicon or another suitable material, according to the team.
Read also: American Medical Association says climate change, public health crisis
They explained that the bubble cluster would be placed in outer space at a Lagrange Point, where the Sun’s and Earth’s gravitational pulls create a stable orbit, adding that if the plan becomes a reality in the future, the completed array would be roughly the size of Brazil.
They admitted that one of the main concerns with their proposal would be the logistics of fabricating a large film, transporting it into space, and then unfolding it to form the bubble raft, suggesting that fabricating the spheres in outer space minimizes shipping costs.
“The bubbles can be intentionally destroyed by breaking their surface equilibrium, this would make the solar geoengineering solution fully reversible and significantly reduce space debris,” the researchers said
The researchers who further pointed to the difficulties of maintaining the integrity of the bubble shield noted that an effective replenishment rate will be studied to ensure the shield maintains its size, together with strategies to guarantee a smooth end-of-life transition.
Story was adapted from GISMODE.